Density Dilemma
RETIRED BETA VERSION - For current versions of the SciGen materials, please visit serpmedia.org/scigen
GOING THROUGH PHASES
Density is a defining characteristic of a substance, but it's not a constant. Substances will always have the same density at the same temperature. At a certain temperature, density is a constant that can be measured and compared. Scientists often test the density of a substance at room temperature.
Solid, Liquid, Gas
Heat and pressure both can change the phase of a substance: usually from a solid to a liquid to a gas. Sometimes solids change directly to gases (a process called "sublimation.")
Evaporation (changing from a liquid to a gas) and condensation are both physical changes. More specifically, they are phase changes. Phase changes are changes between the solid, liquid, and gaseous forms of a substance. The most familiar example of phase changes is water:
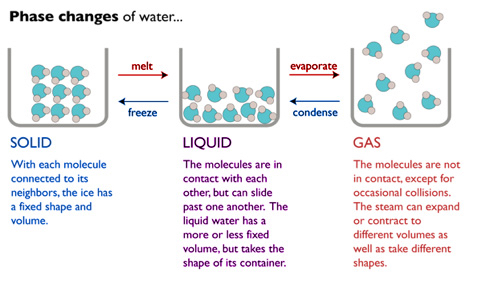
Liquid: Condensed and Fluid
Solids and liquids are both condensed phases of matter, with particles in continuous contact with each other. Liquids and gases are both fluid phases of matter, with particles able to change position relative to each other.
condensed matter 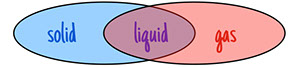 fluid matter
fluid matter
Notice that liquids are both condensed and fluid!
Changing a Nail
When an iron nail rusts, it undergoes a chemical reaction. But when it bends, that’s just a physical change, not a chemical reaction. There’s no change in chemical composition: It’s still just a bunch of iron atoms.
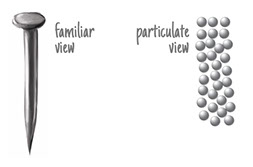
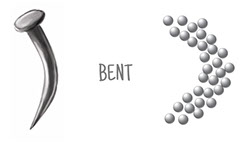
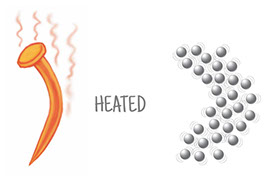
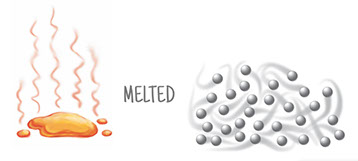
Look again at the three illustrations of iron atoms at different temperatures. All the iron atoms are the same size, and there are 31 of them in each illustration. Those atoms take up more space as they heat up, move faster, and bounce off each other harder. There are the same number of atoms, just spread out more. The temperature in the last image is hot, hot, hot! The melting point of iron is 2800°F (1538C), a temperature not seen on Earth, but common inside its core.
 TURN AND TALK
TURN AND TALK
Each of the three illustrations has a square drawn over it. The three squares are the same size. What happens to the number of atoms inside the squares as you go from cooler to hotter?
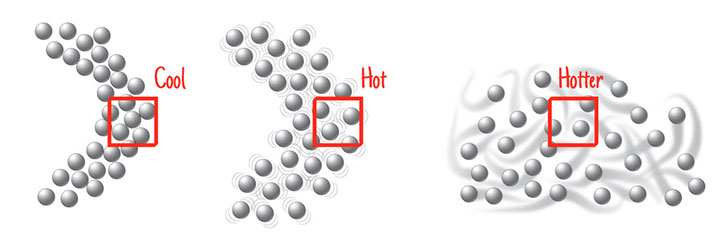
As an iron nail heats up and expands its overall volume, one cubic centimeter of its substance has fewer atoms. With fewer atoms, one cubic centimeter of its substance has less mass, even though the overall mass of the expanded object is the same as before.
The ratio of mass to volume is called density. Put another way, density is mass divided by volume. So an iron nail becomes less dense as its temperature climbs.
Density = Mass / Volume
Density is often measured in grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm3).
Iron at room temperature has a density of about 7.87 g/cm3. For the following questions, assume the iron remains at room temperature.
- What is the mass of three cubic centimeters of iron at room temperature?
- What is the volume of 15.74 grams of iron at room temperature?